How to Improve Retention: The Ultimate Guide for Product Managers and Leaders
After 15+ years in product and analyzing the world's best retaining companies, what have I learned - and what do I recommend you do? Let's cover the key strategies, tactics, and orgs to make it happen
Retention is the ultimate measure of product-market fit.
Usually, the problem of solving and improving retention is the CEO and CPO’s to own first and foremost. But, it’s also the job of everyone at the company to contribute to and execute on.
In today’s guide, we’re going to cover my hard-won lessons from 15+ years of working on and improving retention. Along the way, I helped:
Fortnite increase 30D retention by over 10%
thredUP increase CLV by over 40%
Affirm increase TPU by over 50%
We’ll explain exactly what I contributed to all of that in today’s guide.
Brought to you by ChurnKey
Churnkey is a retention automation platform that reduces churn, recovers failed payments, and drives more revenue for companies built on recurring revenue. PLG SaaS Companies like Jasper, Veed.io, Copy.ai, and more rely on Churnkey to reduce churn and improve retention.
Churnkey integrates directly with payment platforms, like Stripe and Chargebee. They work with any company that has a very high volume of subscriptions.
So if you optimize for self-serve onboarding, Churnkey would be a great platform to optimize your cancellation flows, failed payment recoveries, and reactivations.
Today’s Post
Words: 8,556 | Est. Reading Time: 38 Mins
This post has been over 2 months in the making. After consulting numerous of my own prior documents and friends, I’m ready to present this retention masterclass:
How to Measure Retention Correctly
The Retention Hierarchy of Needs
Whose Problem is Retention?
6 Case Studies in Success
How to Organize Your Teams
Encyclopedia of Retention Tactics
1. Measuring Retention Correctly
Measuring retention seems simple, but for anyone who’s actually done it, they know: there’s lots of intricacies in reality.
I boil it down to 3 main steps that you’ll need to take (and I recommend using your logs and going and doing this, instead of taking your company’s definition):
Isolate cohorts
Determine what counts as an active user
Decide which time period to measure
Let’s go through each one by one.
Step 1 - Isolate cohorts
Every retention measurement starts with isolating cohorts. You need to figure out the bucket of people’s retention you care about.
The most common way is to group new users you acquire each week or month. But you don’t always need to look at new users.
And you don’t always look at a time dimension. You will often look at things like region, acquisition channel, or device.
The key here is to choose cohorts that make sense for your business. If you're a global company, regional cohorts might reveal important differences. If you're heavily invested in multiple marketing channels, segmenting by acquisition source could be eye-opening.
Step 2 - What action counts as an active user
The next step is to ask who your active users are really going to be. Traditionally, people will look at if they opened the app or visited the site.
It seems fine, right?
The problem is that someone could just open the app on accident and close it. And advertisers could just drop them on the website when they don’t want to be there.
As a result, most sophisticated companies these days often use a specific feature. For instance, using the most commonly used feature of value:
At Fortnite, actually loading into a game.
At Affirm, actually viewing a merchant or loan.
At Apollo, having any relevant event in any of our products in addition to a view.
This approach gives you a much more accurate picture of who's truly engaging with your product. But it's not one-size-fits-all. You need to think critically about what actions truly represent value for your users.
My general guidance here is: the best action touches your most common source of user value.
For Instance,
Instagram used ‘viewed 3 or more posts’. This avoids people seeing 1-2 who just open it and then close.
Uber chose completed a ride
These choices are deliberate. They're looking for actions that signify real engagement, not just casual or accidental use.
Now, here's something that might surprise you: just using something like is paying is not the answer. Usually, is paying + someone in the account is an active user is better
That’s because a company could be paying for your B2B software, but if no one's using it, that's not true retention. You're at risk of churn. What you really want is paid accounts where people are actively engaging with your product.
In the B2B world, you might have multiple users under one account. Do you care if the account is retained (i.e., keeps paying), or do you care about individual user retention within that account? Often, it's both – you want the account to stay, and you want users within that account to remain active.
Step 3 - Which time period to measure
Now that you've nailed down who you're measuring and what counts as active, you need to decide on your time frame. This isn't as straightforward as it might seem.
Different products have different natural usage cycles:
Social media apps might look at daily active users (DAU)
B2B SaaS products might focus on weekly or monthly active users (WAU or MAU)
Seasonal products (like tax software) might look at annual retention
The key is to choose a period that aligns with your product's expected usage patterns. Don't set unrealistic expectations – if your product isn't designed for daily use, don't measure daily retention.
It's also worth considering multiple time frames. For example:
Short-term retention (7-day or 30-day) can give you quick feedback on new features or onboarding changes.
Long-term retention (90-day or annual) can provide insights into overall product stickiness and lifetime value.
By looking at both, you can get a more complete picture of your retention dynamics.
The Charts Once You Have the Data
Alright, you've done the hard work of collecting and organizing your retention data. But let's face it: staring at a data table isn't going to win you any friends in the boardroom. When it comes to retention, you want to visualize the data in a way that tells a story. Let's dive into the charts that will make your retention data sing.
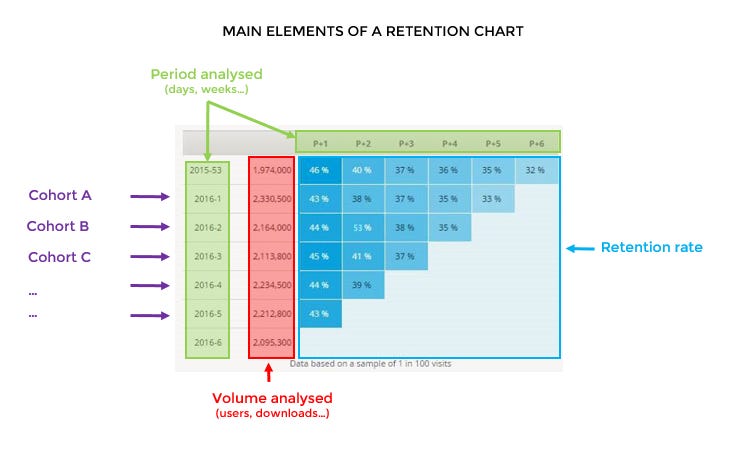
1. New Users - Divide by Each Subsequent Month
This is your ground zero, the foundation of all retention analysis.
What’s happening here?
Left Side - Month they came from
January
February
March (and so on, marching down the left side of your table)
Right Side - Which month they came from, so each column is a '+'
Month 0 (always 100%, your starting point)
Month 1 (cue the suspense)
Month 2 (the plot thickens) (continuing across to the right)
This table is your retention story in its rawest form. It's not glamorous, but it's powerful. You can see at a glance how each cohort performs over time. But let's be honest, tables are the vegetables of the data world - nutritious, but not always appetizing. So let's move on to the main course.
2. Cohort Retention Curves
Now we're talking! This is where your data starts to look sexy. Imagine a line graph where:
Each line represents a cohort (maybe January is blue, February is red, and so on)
The x-axis shows time (usually in months)
The y-axis shows the retention rate
What you're looking for here is the shape of those lines. Are they:
Dropping off a cliff in the first month? (Yikes, might want to look at your onboarding)
Gradually flattening out? (That's more like it)
Crossing each other? (Ooh, intrigue! Later cohorts performing better or worse?)
This is where you start to see the patterns emerge.
3. Layer Cake Graphs
Finally, take your cohort retention curves, but instead of just lines, fill in the area under each line. Voila! You've got a layer cake graph.
Why "layer cake"? Because each cohort forms a layer, and together they build up like a delicious, data-driven cake. This graph is a feast for the eyes, showing you:
The total volume of retained users (the height of your cake)
How much each cohort contributes to your current user base (the thickness of each layer)
Whether newer cohorts are forming thicker layers (Is your cake getting taller over time? Yum!)
What is Good Retention?
So what does "good" retention actually look like?
Generally, you want your retention curve to flatten out. Think of it like a roller coaster - a steep drop at the beginning is normal (and maybe even fun), but you don't want it to keep plummeting forever. You're aiming for that nice, gentle glide at the end.
What’s even better?
The Flat (or Rising!) Retention: The best of the best see cohort retentions that are flat and then - wait for it - actually start increasing. Yes, you read that right. It's like your users are aging like fine wine, getting better (more engaged) over time.
The Improving Cohorts: You want to see subsequent cohorts getting better over time. It's like each new batch of users is an improved recipe - retaining better than the last.
Of course, the whole point of this data feast isn't just to make pretty charts (though that is a nice side benefit). It's to improve your product. So how do you go from "ooh, pretty graphs" to "aha! I know what to do"?
The key is to cut your data by different cohorts. Don't just look at time-based cohorts. Get creative:
Acquisition channel (Did those Facebook ads really pay off?)
User demographics (Are millennials sticking around longer than Gen Z?)
Product version (Did that big redesign help or hurt?)
Feature usage (Are power users who use Feature X retaining better?)
Each of these cuts is like a different lens on your retention microscope. The more lenses you use, the more likely you are to spot the retention bacteria you need to zap (or the retention superfoods you need to cultivate).
So with those basics covered, let’s move on to my main mental model to moving retention.
2. 6 Case Studies in Success
You can’t actually move retention. If you have low retention, you’re screwed.
This might be the worst advice I have ever heard. Yet so many people repeat it. Let’s walk through 3 of my own case studies of moving retention, and 3 case studies that companies have generously shared.
Case Study 1 - Fortnite
Let’s start with case studies that were my own.
At Fortnite, we faced a unique challenge: keeping players engaged in a highly competitive gaming environment. Our approach went beyond just creating fun gameplay.
We kicked off with a focus on daily engagement. Challenges and events gave players reasons to log in regularly. This simple addition created a powerful loop, bringing users back day after day.
Habit formation was our next target. We refined our notification strategy, ensuring players knew when friends were online or special events were happening. These timely nudges became the triggers for regular gameplay sessions.
One of our most effective moves was counterintuitive: we made dying more fun. In a battle royale, most players lose most of the time. By adding entertaining death animations and quick re-queue options, we turned potential frustration into part of the fun. It's a reminder that every aspect of user experience, even the seemingly negative ones, can be optimized for retention.
Our retention strategy extended beyond the game itself. We built out the creator and competitive ecosystem, creating a YouTube-powered flywheel that kept players engaged even when they weren't in the game. This taught us to look beyond our core product for retention opportunities.
Finally, we tackled mobile retention. By improving usability and gameplay on lower-end devices, we ensured a great experience for all players. It was a crucial lesson in not neglecting any segment of your user base.
Three key elements defined our strategy:
Daily engagement through challenges and events
A robust notification system to form habits
An ecosystem that extended engagement beyond the game
The result? A 10% increase in 30-day retention. In the hyper-competitive world of gaming, that's a massive win.
Case Study 2 - Spotify
When Spotify launched in 2008, the music industry was still reeling from piracy issues. Their challenge wasn't just getting users to sign up, but keeping them engaged month after month.
Spotify's journey to retention mastery is a tale of personalization and social connection:
2015: The Year of Personalization
Spotify introduced Discover Weekly, a personalized playlist updated every Monday. This feature was a game-changer. As Matthew Ogle, then Spotify's product director, put it: "It's like having your best friend make you a mixtape every single week."
Within the first year, 40 million users had streamed over 5 billion tracks from Discover Weekly playlists.
2017: Turning Music into a Social Experience
Spotify launched its social features, including Friend Activity and Collaborative Playlists. This tapped into the fundamental human need for connection.
By 2018, 40% of all Spotify listening time came from user-generated playlists.
2019: Beyond Music
Recognizing the growing popularity of podcasts, Spotify made a bold move by acquiring Gimlet Media and Anchor for $340 million.
By 2021, Spotify had become the most popular podcast platform in the U.S., surpassing Apple Podcasts.
The result of these efforts was impressive: Spotify achieved a 73% retention rate after the first month, significantly outperforming the industry average of 45-55% for music streaming apps.
Case Study 3 - thredUP
At thredUP, we faced the challenge of not just acquiring customers, but keeping them coming back. Our focus was on increasing customer lifetime value (CLV).
We started by lowering the barrier to entry. Strategic price reductions on key items made it easier for new customers to make their first purchase.
Next, we implemented comprehensive lifecycle marketing. We crafted growth marketing email sequences that nurtured customers throughout their journey. This was complemented by strategic promotions and remarketing ads to re-engage customers.
User experience improvements played a crucial role. We enhanced our filtering system and introduced saved preferences, reducing friction for return visits. We also introduced an outfits tool, adding value beyond our core offering.
Throughout our efforts, we doubled down on personalization. Improved merchandising algorithms showed customers more of what they were likely to love.
Our retention strategy hinged on three key innovations:
Improved filters and saved preferences for seamless return visits
An outfits tool to inspire and increase basket sizes
Personalized merchandising to enhance relevance
The results were significant. Between 2014 and 2017, we saw a 40% increase in CLV. This wasn't just a vanity metric - it unlocked a whole new phase of growth. It led to higher customer acquisition costs (CAC) balanced by higher LTV, enabling more aggressive marketing and a faster growth rate. Ultimately, this success helped secure our Series D investment.
Case Study 4 - Duolingo
Duolingo entered the market in 2012 with a mission to make language learning free and accessible. Their challenge was keeping users engaged in something as challenging as learning a new language.
Duolingo's retention strategy revolves around gamification and habit formation:
2013: The Streak is Born
Duolingo introduced the streak feature, encouraging daily usage. As co-founder Luis von Ahn explained, "The streak is the single most powerful thing we have to get people to come back."
By 2020, over 1.5 million users had a streak of 365 days or more.
2019: Competitive Learning
The introduction of Leagues added a competitive element, grouping users based on their XP earned each week.
In the first year after launch, users who joined Leagues completed 72% more lessons on average.
2020: Expanding the Ecosystem
Duolingo launched its podcast and virtual events, creating a more comprehensive language learning environment.
The Duolingo Spanish Podcast reached #1 on the US iTunes podcast charts for all categories.
Duolingo's retention strategy was anchored by these key elements, resulting in a retention rate of 55-60%, far exceeding the EdTech industry average of 30-40%.
Case Study 5 - Affirm
At Affirm, our goal was to increase transactions per user (TPU). We needed to make Affirm an integral part of shopping habits.
We started by expanding our merchant network. Partnerships with popular platforms like Shopify and Amazon increased usage opportunities.
Next, we developed a mobile app. It served as a hub for Affirm activity and a discovery tool for enabled merchants.
We also introduced the "Pay in 4" option with zero interest. This lowered the barrier for frequent, smaller transactions.
Throughout, we maintained a focus on showing value and forming habits after the first use.
Our retention strategy revolved around three key areas:
Expanding our merchant network for increased accessibility
Developing a feature-rich mobile app
Offering flexible payment options to meet diverse needs
The result was impressive: a 50% increase in TPU.
Case Study 6 - Strava
Strava, launched in 2009, entered a crowded fitness app market. Their challenge was making people stick to their fitness goals and choose Strava over countless alternatives.
Strava's retention strategy focused on community building and competitive elements:
2010: Segments - Turning Every Route into a Race
Strava introduced Segments, allowing users to compete on specific routes. As co-founder Mark Gainey said, "Segments allowed us to gamify the entire world."
By 2020, users had created over 180 million Segments worldwide.
2016: Beacon - Safety Meets Social
The introduction of Beacon, a safety feature allowing real-time location sharing, added a new dimension to the app.
Beacon usage increased by 30% in 2020, highlighting its importance to users.
2020: Personalized Route Suggestions
Strava launched Routes, using AI to suggest personalized routes based on user preferences and community data.
Within the first year, over 20 million Routes were created by users.
The result of these efforts was remarkable: Strava achieved an 80% annual retention rate, far outperforming the fitness app industry average of 25-35%.
These case studies demonstrate that while the specifics may vary, successful retention strategies often share common themes.
Let’s concretize all the learnings from these case studies into a framework.
3. The Retention Hierarchy of Needs
Too often, teams jump to advanced retention tactics before nailing the basics. If your core product isn't delivering value, no amount of clever notifications or gamification will save you.
One of my go-to concepts for solving a retention problem is starting with a retention hierarchy of needs.
This means thinking of retention as a pyramid, where you have to satisfy the lower layers first before tackling the one’s above them:
Here’s what’s essential to know about each layer.
Layer 1: Core Value Delivery (The Foundation)
If you can’t build:
A great core product
Excellent onboarding into it
You’re generally toast is it’s related to retention over the long-term.
This is the bedrock of your product. If you're not nailing this, nothing else matters.
You’ll be surprised. But as companies expand, this area is often a problem.
The solutions lie in your core product teams, but you can also deploy a growth activation team. These teams often rely on tactics like:
Improve your UX and information architecture
The activation playbook
The metrics that go alongside this are:
Time to Value (TTV)
First Value Experience (FVE) completion rate
Core action completion rate
This is the first layer of the hierarchy of needs - and going to a later layer is usually not worth your time until it’s nailed.
Layer 2: Engagement (The Building Blocks)
Once users get your core value, it's time to keep them coming back for more. This is where your core product teams really prove their mettle.
Engagement turns one-time users into regulars. It's the difference between a fling and a long-term relationship.
And it’s measured by tried-and-true metrics like:
Daily Active Users / Monthly Active Users (DAU/MAU)
Session frequency
Time spent in app
If you’re working to move this, you’ll want to do things like:
Create more regular use cases
Create reasons to keep coming back
It’s the second layer - important to get right before you move on.
Layer 3: Habit Formation (The Keystone)
This is where your product becomes part of users' daily lives. It's not just useful; it's necessary.
Habits are hard to break. When your product becomes habitual, you've achieved a new level of stickiness.
Working in this layer entails doing things like:
Integration with Daily Routines: Becoming part of existing behaviors.
Creation of New Rituals: Establishing new behaviors centered around your product.
Leveraging Existing Habits: Piggybacking on habits users already have.
The metrics that are relevant here are things like:
Retention curve flattening
Usage frequency patterns
Feature adoption rates over time
When the core product itself doesn’t deliver, adding growth tactics can be very useful:
Implement daily streaks or challenges
Create time-based triggers (e.g., "Your daily summary is ready")
Offer cross-platform consistency for seamless integration into users' lives
Habit formation is is a major unlock - and many of the product businesses that we all admire, like Figma and Notion, have nailed it.
Layer 4: Churn Prevention (The Fortification)
Once you've got users hooked, many people stop there. But it’s a mistake. Keeping paying users long-term usually requires active defense against churn.
And this matters. It's far cheaper to keep existing users than to acquire new ones.
There’s basically two types of churn prevention:
Voluntary Churn Reduction: Addressing active decisions to leave.
Supported by tactics like:
Implement exit surveys
Design thoughtful cancel flows
Offer timely retention offers
Involuntary Churn Prevention: Tackling passive user loss (e.g., payment issues).
Supported by tactics like:
Develop smart payment retry logic
Create effective dunning campaigns
Implement in-app payment recovery
Churn prevention isn't just about stopping users from leaving; it's about continuously demonstrating your product's value.
The metrics that matter here are things like:
Overall churn rate
Voluntary vs. involuntary churn rates
Winback rate
It’s not something you focus on right away - but at a certain scale, it’s a must
Normally there would be a paywall here. But thanks to Churnkey, this entire deep dive is free for all subscribers. Get your free churn reduction analysis by talking to their sales team.
4. Whose Problem is Retention?
Let me make a bold statement: Retention is primarily the job of the product team.
Yes, Retention is everyone’s problem. But I recommend product leaders and teams see themselves as the team most responsible for it — at least in tech, product-driven businesses.
On top of that, this is the way I recommend breaking it down:
CEO : Responsible for the company strategy
CMO: Responsible for acquiring people in the ICP
Product Leader (CPO/VP): Responsible for organizing the teams and setting the strategy for how to achieve retention via the product
Product Managers: Responsible for validating the strategy in their area and making changes for retention of their surfaces
The role of the Product Leader
Product leaders face unique challenges in driving retention:
They need to work closely with the CEO and other leaders to build conviction on organizational structure. This isn't just about org charts - it's about aligning the entire company around retention.
Understanding the role of the growth team (if there is one) is crucial. What are they focused on? How does their work intersect with core product teams? This clarity is essential for a cohesive retention strategy.
Perhaps most importantly, they need to ensure each core product team is focused on the right layer of the retention hierarchy. Are they working on core value delivery when they should be tackling habit formation? This misalignment can derail retention efforts.
Product leaders must also push teams to derisk solutions to top retention problems. It's not enough to identify issues - teams need clear, validated paths to solving them.
The role of the product manager
For Product Managers, retention is a daily battle:
They need to be proactive in thinking about their layer of focus in the retention hierarchy. Is their product area still struggling with core value delivery, or is it time to level up to engagement or habit formation?
Constantly driving higher feature adoption is key. But it's not just about usage numbers - it's about understanding how feature adoption translates to the retention that matters for the business.
PMs need to see the bigger picture of how their area drives overall retention. This means understanding not just their metrics, but how they fit into the company's broader retention goals.
They should be retention evangelists, constantly pushing their teams to think about how every decision impacts user retention. This mindset can be the difference between a product that users tolerate and one they can't live without.
Remember, retention isn't solved once and forgotten. It's an ongoing process of learning, iterating, and improving. The product team needs to be relentless in their pursuit of keeping users engaged and coming back for more.
5. How to Organize Your Teams
When it comes to retention, how you structure your teams can make or break your efforts. Let's dive into some key approaches:
Organizing by Metrics vs. Features
There's no one-size-fits-all approach here. Some companies swear by metric-based teams, while others stick to feature-based organization. Both can work, but they come with trade-offs.
Metric-based teams focus on moving specific numbers. You might have a "Day 7 Retention" team or a "Monthly Active Users" team. This approach keeps teams laser-focused on outcomes. But it can lead to short-term thinking or feature bloat if you're not careful.
Feature-based teams own specific parts of the product. They're responsible for how their feature area impacts overall retention. This can lead to more cohesive product development, but you risk teams losing sight of the bigger retention picture.
My take? A hybrid approach often works best. Have core feature teams, but make sure they're aligned on key retention metrics.
Setting Retention OKRs
Whatever your team structure, setting clear Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) for retention is crucial.
At the company level, you might have an objective like "Become the stickiest product in our category." Key results could include improving 30-day retention by X% or increasing daily active users by Y%.
For individual teams, tailor the OKRs to their area of influence. A messaging feature team might aim to increase message send frequency, knowing this drives overall app retention.
The key is making these OKRs challenging but achievable. Sandbag them, and you're not pushing hard enough. Make them impossible, and you'll demoralize your teams.
Retention Teams vs. Core Teams
Here's where it gets spicy. Should you have dedicated retention teams?
In my experience, a pure retention team can be a double-edged sword. On one hand, they can dive deep into retention data and experiments. On the other, they risk becoming a crutch for core teams who might think, "Retention? Not my problem."
Instead, consider a growth team focused on activation. They can work on that crucial first-time user experience, setting the stage for long-term retention. This team can partner with core teams, bringing a retention-first mindset to feature development.
But don't let core teams off the hook. They should still own their feature's impact on overall retention. The growth team is there to support, not to take over.
The Retention Council
One structure I've seen work well is a "Retention Council." This cross-functional group meets regularly to discuss retention challenges and align on strategies.
Include representatives from product, engineering, data science, and even marketing. This ensures retention stays top of mind across the org and facilitates knowledge sharing.
The council can set the overall retention strategy, while individual teams execute within their domains.
Remember, there's no perfect org structure for retention. The key is to make retention everyone's responsibility, provide clear metrics and goals, and foster cross-team collaboration.
Now let’s give you a complete taxonomy of all the retention tactics to consider.
6. Encyclopedia of Retention Tactics
The overall approach is the product process - talk to customers, discover problems and obstacles to getting habitual value, then solve them
But it can be useful to be able to refer to tests.
Here they are:
Layer 1: Core Value Delivery
Onboarding
1. Personalized Welcome Flows
Tailor the onboarding experience based on user characteristics or stated goals. This isn't just about showing different screens - it's about fast-tracking users to their "aha" moment.
Implement by segmenting users during sign-up. Ask for key information like job role, main goals, or experience level. Use this data to customize the initial product tour, feature recommendations, and even default settings.
Duolingo excels at this. They ask users about their language learning goals and experience, then adjust the difficulty and lesson plans accordingly. This personalized approach contributed to their impressive 55% D1 retention rate.
2. Interactive Tutorials
Get users to actually perform the core actions that deliver value. It's the difference between watching a cooking show and actually making the dish.
Design tutorials that require users to complete mini-tasks within your product. Ensure each task teaches a key feature while moving the user towards their goal.
Figma's interactive tutorial guides new users through creating and editing a design, teaching core tools along the way. This hands-on approach helps users quickly grasp the power of the platform.
3. Progress Bars
Tap into the Zeigarnik effect. Show users how close they are to unlocking full product value. It's not just a visual - it's a psychological trigger for completion.
Implement a clear, visually appealing progress bar during onboarding. Break down the process into 5-7 clear steps. Ensure each step provides value, not just busywork.
LinkedIn's profile completion bar is a classic example. It nudges users to add more information, improving both the user's profile and LinkedIn's data richness. This feature reportedly increased profile completeness by 55%.
4. Onboarding Checklists
Provide a clear roadmap for new users to follow. It's not about hand-holding - it's about empowering users to explore your product purposefully.
Create a checklist of 5-10 key actions new users should take. Make it easily accessible, perhaps pinned to the dashboard. Allow users to dismiss it, but make it easy to retrieve.
Asana's "Get Started" checklist guides new users through creating tasks, assigning them, and setting due dates. This ensures users engage with core features quickly.
5. Contextual Help Bubbles
Don't force users to dig through help docs. Bring the information to them when and where they need it.
Implement smart, context-aware help bubbles that appear when users hover over or interact with new features. Keep the content concise and actionable.
Slack uses this effectively, providing quick explanations of features like channels or direct messages as users encounter them for the first time.
First Value Experience
6. Quick Wins
Design features that deliver immediate, tangible value. Think Canva's ready-made templates or Slack's Slackbot welcome message. It's about creating a "wow" moment within seconds, not minutes.
Identify your product's core value proposition. Then, design a feature that delivers a slice of that value with minimal user input.
Canva's template library lets users create professional-looking designs in minutes, even with no design skills. This quick win keeps new users engaged and coming back.
7. Frictionless Core Action
Ruthlessly eliminate steps between sign-up and core value delivery. Every click is an opportunity for users to drop off. Make your core action so easy, it feels like falling off a log.
Map out your user's journey to core value. Then, ruthlessly eliminate or automate any unnecessary steps. Aim to reduce time-to-value by at least 50%.
Twitter's "What's happening?" prompt on the home page enables users to post immediately after signing up. This frictionless approach to the core action of tweeting has been key to Twitter's user engagement.
8. Value Visualization
Show, don't tell. Visualize the impact of using your product. Whether it's money saved, time freed up, or problems solved - make the value concrete and undeniable.
Create data visualizations that clearly show the benefits of using your product. Use comparison charts, progress trackers, or impact meters.
Mint's financial overview dashboard visualizes a user's entire financial life, making the value of using the app immediately apparent. This clear value demonstration contributes to user retention.
9. Preset Configurations
Don't make new users start from scratch. Provide intelligent default settings that deliver value immediately.
Analyze your power users' configurations. Use these insights to create preset options that work well for different user segments. Allow easy customization later.
Notion's templates provide preset configurations for various use cases, from personal task management to team wikis. This helps new users see the platform's potential quickly.
10. Immediate Integration
If your product relies on data or connects with other tools, make that connection instant and painless.
Implement one-click integrations with popular tools in your space. Use OAuth for seamless authorization. Show a real-time preview of the value this connection provides.
Zapier's quick integrations allow users to set up powerful automations in minutes. This immediate value delivery has been crucial to their growth and retention.
Layer 2: Engagement
Feature Discovery
11. Contextual Feature Tips
Don't overwhelm users with all features at once. Introduce advanced features when they're most relevant. It's about right time, right place - not information overload.
Use behavioral triggers to introduce features. If a user repeatedly performs a task manually, suggest a feature that could automate it. Keep suggestions brief and dismissible.
Grammarly does this well, introducing more advanced writing suggestions as users engage more with the platform. This tiered approach keeps users discovering new value over time.
12. User-Triggered Walkthroughs
Let curious users explore on their own terms. Provide on-demand guides for different features. It's choose-your-own-adventure, not a forced march through your product.
Create a help center with interactive guides for each major feature. Make it easily accessible from within the product. Use tooltips to let users know these guides exist.
Airtable's on-demand video tutorials for different features allow users to learn at their own pace. This self-serve approach caters to different learning styles and usage patterns.
13. Feature Spotlights
Regularly highlight features that users haven't engaged with yet. It's not about pestering - it's about revealing hidden value.
Implement a "Feature of the Week" section in your product or email communications. Briefly explain the feature's benefits and provide a quick how-to.
Evernote regularly spotlights features like Web Clipper or document scanning, helping users discover the full potential of the app over time.
14. Progressive Feature Rollout
Don't dump your entire feature set on new users. Gradually introduce complexity as users become more proficient.
Map out a logical progression of feature complexity. Unlock advanced features based on usage milestones or time spent in the product. Always provide the option to "unlock all" for power users.
Duolingo progressively introduces more complex language constructs and features like Stories or Podcasts as users advance, keeping the learning curve manageable.
15. Contextual Empty States
Turn empty states into opportunities for feature discovery. Don't just show a blank page - guide users to relevant actions.
Design informative and actionable empty states for each section of your product. Include a brief explanation of the section's purpose and a clear CTA to populate it.
Trello's empty board state suggests creating lists and adding cards, guiding new users to engage with the core functionality immediately.
Regular Use Cases
16. Daily/Weekly Digest Emails
Don't rely on users remembering to check your product. Bring valuable insights directly to their inbox. But remember, it's not about bombardment - it's about delivering genuine value on a silver platter.
Analyze user behavior to identify key metrics or updates they care about. Create templated emails that populate with personalized data. Allow users to customize frequency and content.
Strava's weekly activity reports summarize a user's exercise data, comparing it to previous weeks and friends' activities. This regular touchpoint drives users back to the app.
17. Recurring Task Automation
Identify repetitive tasks users perform and offer to automate them. It's not just about saving time - it's about making your product an indispensable part of their workflow.
Use pattern recognition to identify tasks users perform regularly. Offer to automate these tasks, showing the time saved. Make it easy to modify or disable automations.
IFTTT's applets automate recurring tasks across various platforms. By becoming the glue between different services, IFTTT embeds itself deeply in users' digital lives.
18. Scheduled Reminders
Help users build habits around your product. Offer to set reminders for key actions or check-ins.
Implement a reminder system that users can easily set up. Allow customization of frequency and delivery method (push notification, email, etc.). Always provide clear value with each reminder.
Headspace, the meditation app, allows users to set daily reminders to meditate. This feature helps users build a consistent practice, driving retention.
19. Personalized Dashboards
Create a home base that users want to check regularly. Highlight the most relevant information and actions for each user.
Use machine learning to identify the metrics, features, or content each user engages with most. Automatically adjust dashboard layouts to prioritize this content. Allow manual customization as well.
Netflix's personalized homepage, which adjusts based on viewing history, keeps users engaged by always presenting relevant content upfront.
20. Integration with Daily Tools
Embed your product into the tools your users already use every day. Become part of their existing workflows.
Develop integrations or plugins for popular productivity tools, communication platforms, or industry-specific software. Ensure these integrations provide clear value, not just a bolt-on presence.
Slack's integrations with tools like Google Drive, Trello, and GitHub make it a central hub for many teams' daily workflows, driving consistent engagement.
Layer 3: Habit Formation
Triggers
21. Smart Notifications
Don't notify for the sake of it. Use behavioral data to send perfectly timed, relevant nudges. It's the difference between an annoying ping and a welcome reminder.
Implement a notification system that learns from user behavior. Use AI to predict the best times and content for notifications. Always provide clear value and an easy way to act on the notification.
Spotify's Discover Weekly playlist, delivered every Monday, has become a habit-forming feature for many users. It's timely, personalized, and delivers clear value.
22. Streaks and Challenges
Gamify consistent usage without feeling gimmicky. Tap into users' intrinsic motivation to maintain streaks or complete challenges. It's not about cheap tricks - it's about aligning product use with personal goals.
Implement a streak system for key actions in your product. Create time-bound challenges that encourage exploration of different features. Always tie these back to the core value of your product.
Duolingo's streak feature, which tracks consecutive days of language learning, has been a key driver of daily active usage. Users become motivated to maintain their streaks, forming a strong daily habit.
23. Social Proof Notifications
Leverage the power of FOMO (Fear of Missing Out). Show users how others are benefiting from regular product use.
Implement a system that notifies users of relevant activity from their network or similar users. Be careful to maintain privacy and provide genuine value, not just noise.
LinkedIn's notifications about profile views or job changes in one's network drive regular check-ins and engagement with the platform.
24. Ambient Awareness Features
Keep your product on users' radar without being intrusive. Create subtle reminders of your product's presence and value.
Develop unobtrusive widgets, browser extensions, or desktop apps that provide value without requiring the user to open your full product. Focus on providing quick, useful information or actions.
Grammarly's browser extension provides constant, subtle value by checking writing across various websites. This ambient presence keeps the product top-of-mind.
25. Contextual Triggers
Use external factors or user behavior to trigger engagement at the most relevant moments.
Implement a system that monitors relevant external data (time, location, weather, etc.) or user actions in other apps. Use this data to trigger timely, valuable interactions with your product.
Uber's surge pricing notifications, triggered by high demand in a user's area, create a sense of urgency and drive immediate engagement.
Reward Loops
26. Progress Milestones
Celebrate user achievements, no matter how small. But go beyond just badges - show the tangible impact of their progress. It's not vanity metrics - it's validating their investment in your product.
Identify key milestones in your user journey. Create a reward system that celebrates these achievements with tangible benefits. Always tie the celebration back to the value the user has gained.
Codecademy's progress tracking and certificates provide a sense of achievement as users advance through courses, encouraging continued engagement.
27. Unlockable Features
Gate advanced features behind usage milestones. But be careful - this isn't about frustrating users. It's about pacing the complexity and maintaining a sense of discovery.
Identify advanced features that might overwhelm new users. Create a logical progression of feature unlocks tied to usage milestones. Always provide the option to "unlock all" for power users.
Kahoot!, the learning platform, unlocks more advanced quiz creation features as users create and host more quizzes. This gradual unveiling keeps users engaged and learning over time.
28. Tiered Loyalty Programs
Create a sense of progression and exclusivity. Reward your most engaged users with tangible benefits.
Develop a tiered system with clear benefits at each level. Make progress visible and achievable. Ensure rewards are genuinely valuable, not just symbolic.
Sephora's Beauty Insider program, with its tiered rewards and exclusive offers, has been a key driver of customer retention and increased purchase frequency.
29. Community Recognition
Tap into users' desire for status and recognition. Highlight top contributors or power users within your product's community.
Implement a system to identify and showcase top users. This could be through leaderboards, featured user content, or special badges. Ensure recognition is tied to valuable contributions, not just usage volume.
Stack Overflow's reputation system and badges recognize users for helpful contributions, driving continued engagement and quality content creation.
30. Surprise and Delight Moments
Keep the experience fresh with unexpected rewards. Create moments of joy that users want to share.
Randomly trigger special rewards or unique experiences for users. These should feel generous and unexpected. Encourage sharing of these moments to create positive word-of-mouth.
Mailchimp occasionally surprises users with playful animations or messages, creating moments of delight in an otherwise routine task of sending emails.
Layer 4: Churn Prevention
Proactive Retention
31. Predictive Churn Modeling
Don't wait for users to have one foot out the door. Use data to identify at-risk users before they even think about leaving. It's not mind-reading - it's smart, preemptive care.
Implement machine learning models that analyze user behavior patterns. Identify key indicators of potential churn. Create automated workflows to re-engage at-risk users with targeted offers or assistance.
Netflix uses predictive modeling to identify users at risk of cancelling and serves them personalized content recommendations to re-engage them.
32. Personalized Re-engagement Campaigns
Generic "We miss you" emails don't cut it. Tailor your re-engagement based on past user behavior and preferences. It's not about guilt-tripping - it's about reminding users of the specific value they're missing.
Segment your at-risk users based on their past behavior and preferences. Create targeted campaigns that speak to the specific value they've received in the past. Offer clear, compelling reasons to return.
Spotify's "Wrapped" campaign, which provides personalized year-in-review summaries, has become a highly anticipated annual event that re-engages even lapsed users.
33. Win-back Incentives
Sometimes users need a little extra push to come back. Offer targeted incentives to reactivate dormant accounts.
Create a tiered system of win-back offers based on user value and churn risk. These could include temporary feature upgrades, account credits, or exclusive content. Always tie the offer back to the core value of your product.
Dropbox offers extra free storage to returning users, providing a tangible incentive to reactivate and re-engage with the service.
34. Usage Dip Interventions
Catch potential churn before it happens by identifying and addressing usage drops.
Implement alerts for significant drops in user activity. Create automated workflows to reach out with helpful content, feature reminders, or offers of assistance. Make it easy for users to get back on track.
Grammarly sends helpful writing tips and feature reminders to users whose activity has dropped, gently nudging them back to regular usage.
35. Proactive Customer Success Outreach
Don't wait for users to ask for help. Reach out proactively to ensure they're getting value.
Implement a system for customer success teams to proactively reach out to users based on usage patterns or upcoming renewals. Provide personalized tips, use case examples, and offers of assistance.
Salesforce's customer success managers regularly check in with clients, offering personalized advice and ensuring they're leveraging the platform effectively. This proactive approach has contributed to their high retention rates.
Voluntary Churn Prevention
36. Exit Surveys
Don't let churned users leave without feedback. But go beyond multiple-choice options. Allow for open-ended responses to uncover unexpected insights. It's not just data collection - it's your product's post-mortem.
Design a brief but insightful exit survey. Include both quantitative and qualitative questions. Make it easy to complete, possibly offering an incentive for detailed feedback.
Zoom implements exit surveys when users downgrade or cancel, using the insights to continually improve their service and address common pain points.
37. Cancellation Flow Optimization
Sometimes, it's not about preventing cancellation, but about leaving the door open for return. Design a cancellation flow that respects the user's decision while highlighting the value they'll be missing.
Create a multi-step cancellation process that reminds users of key features and benefits. Offer alternatives like account pausing or downgrading. Always keep the process respectful and easy to complete if the user insists.
Adobe Creative Cloud's cancellation flow reminds users of the specific tools they've been using and offers tailored discounts, effectively reducing voluntary churn.
38. Graceful Downgrade Options
Sometimes, it's not about preventing churn, but managing it. Offer alternative plans or hibernation options. It's not admitting defeat - it's keeping the door open for future re-engagement.
Develop a range of plan options, including lower-tier and "pause" options. Make it easy for users to adjust their plan rather than cancelling outright. Clearly communicate what features or limits change with each option.
Hulu offers a pause option for up to 12 weeks, allowing users to temporarily stop their subscription without cancelling. This flexibility has helped manage voluntary churn during slow viewing periods.
39. Value Reinforcement Campaigns
Regularly remind users of the value they're getting from your product. Don't assume they remember or notice everything.
Create automated campaigns that highlight personalized value metrics. This could include time saved, tasks completed, or other relevant ROI measures. Time these campaigns to coincide with potential decision points like renewals.
Grammarly sends weekly writing reports, showcasing how many errors were caught and how the user's writing has improved. This regular value reinforcement keeps users engaged and less likely to churn.
40. Last-Chance Retention Offers
When all else fails, a personalized offer might save the relationship. But use this tactic judiciously to maintain its impact.
Develop a system for creating personalized "last chance" offers for high-value users who are about to churn. This could include extended trials of premium features, personalized training, or special discounts. Use data on the user's history to make the offer as relevant as possible.
The New York Times offers personalized discounts to subscribers who attempt to cancel, often convincing them to stay with a lower rate or added benefits.
Involuntary Churn Prevention
41. Smart Dunning Processes
Don't let failed payments turn into lost customers. Implement intelligent retry logic and communication strategies.
Develop a dunning process that attempts to recover failed payments at optimal times. Use machine learning to determine the best retry schedule based on payment history and user behavior. Implement clear, action-oriented communication at each step.
Netflix's smart dunning process includes multiple retry attempts and clear communications about the issue, helping to recover a significant portion of failed payments before they result in involuntary churn.
42. Payment Method Updater Services
Proactively update expired or soon-to-expire payment methods to prevent interruption of service.
Integrate with payment method updater services offered by major card networks. These services automatically update card details when banks issue new cards. Communicate clearly with users about this process to maintain trust.
Spotify uses card updater services to reduce involuntary churn caused by expired payment methods, maintaining uninterrupted service for many users.
43. Backup Payment Methods
Don't rely on a single payment method. Encourage users to add backup options to reduce the risk of failed payments.
Implement a system for users to add and manage multiple payment methods. Clearly communicate the benefits of having a backup method. Make it easy to switch between methods or to allocate them for different purposes (e.g., primary subscription, in-app purchases).
Amazon encourages users to add multiple payment methods and automatically uses backups if the primary method fails, significantly reducing involuntary churn.
44. Pre-Expiration Reminders
Don't wait for a payment to fail. Proactively remind users to update soon-to-expire payment methods.
Implement a system to track payment method expiration dates. Send timely reminders via email, push notifications, or in-app messages. Make the update process as simple as possible, ideally with a one-click solution.
Dropbox sends email reminders when a user's payment method is about to expire, allowing them to update it before any service interruption occurs.
45. Customizable Billing Dates
Allow users to align their billing date with their personal financial schedule. This can reduce the likelihood of insufficient funds issues.
Offer users the ability to choose or change their billing date. Clearly communicate any prorated charges or credits. Consider offering multiple billing date options to cater to different pay schedules.
Many telecom companies, like Verizon, allow customers to choose their bill's due date, reducing late or missed payments due to timing issues.
46. Grace Periods and Account Pausing
Don't immediately churn users due to payment issues. Offer a grace period or temporary account pause to allow time for resolution.
Implement a system that allows for a defined grace period after a failed payment. During this time, maintain service but limit certain high-cost features if necessary. Provide clear communication about the situation and easy options for resolution.
LinkedIn offers a grace period for Premium subscribers with payment issues, maintaining their account status for a short period while attempting to resolve the payment problem.
And that covers the encyclopedia of retention tactics!
Final Words
We've covered a lot of ground in this retention masterclass. From the foundations of measuring retention correctly to the advanced tactics of preventing churn, we've explored the entire spectrum of keeping users engaged and coming back for more.
Remember, retention isn't just a metric - it's the lifeblood of your product.
Key takeaways:
Measure retention correctly
Follow the Retention Hierarchy of Needs
Make retention everyone's responsibility
Organize for success
Leverage the retention tactics encyclopedia
Remember, there's no one-size-fits-all solution to retention. The key is to understand your users deeply, continually test and iterate, and never stop asking how you can deliver more value.
By focusing relentlessly on retention, you're not just keeping users - you're building a sustainable, growing business.
P.S. Still skeptical? Good.
That's the mindset that'll make you an exceptional PM. Keep questioning, keep iterating, and keep focusing on what truly matters to your users.
Sponsored by Churnkey: Churnkey helps subscription companies like Jasper, Veed.io, and Copy.ai, to drastically reduce voluntary and involuntary churn. On average, Churnkey saves companies 20%-40% of subscription revenue that would otherwise be lost to churn.
Want to advertise with product growth? Email productgrowthppp at gmail.
Up Next
I hope you enjoyed that super-deep dive. All in, it took about 65 hours of work. Let me know any feedback you may have.
Other super-deep dives coming up are:
How Lempire Grows
Indian-Origin Tech Companies
How to Answer ‘Why This Company’
We also have some great podcasts with Mirela Mus, Maja Voje, and Jaryd Hermann coming up.
Talk soon,
Aakash